Can Wildlife Cameras Recognize Specific Animals? The Rise of AI-Powered Detection in Conservation
Publish:
2025-10-11 15:28
Source:
https://www.ring-see.com
Exploring the Role of AI and Deep Learning in Species and Individual Identification
The evolution of wildlife monitoring has accelerated with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision technologies. While traditional wildlife cameras rely on passive infrared (PIR) motion detection to record activity, modern systems have introduced intelligent recognition algorithms that can detect, classify, and sometimes even identify individual animals.
This article provides an overview of how these capabilities work, what technologies enable them, and how manufacturers — including Ringsee, a Chinese supplier of intelligent security and wildlife cameras — are contributing to this emerging field.
Limitations of Traditional Wildlife Cameras
Conventional wildlife or trail cameras are designed for trigger-based recording. A PIR sensor activates when detecting movement or temperature changes, capturing images or short video clips. These devices function independently, requiring no network connection or human supervision.
However, traditional systems present several limitations:
They cannot distinguish species; a fox, deer, or human would produce identical triggers.
They generate large volumes of redundant data, including false activations caused by wind or shadows.
They lack behavioral or contextual analysis, preventing detailed ecological insights.
These constraints have led to the integration of AI-assisted processing, transforming passive image collection into active species identification.

AI Integration and Intelligent Recognition
AI-enhanced wildlife cameras utilize deep learning models — primarily convolutional neural networks (CNNs) — to interpret image content. These models are trained on extensive datasets containing labeled animal images captured under various environmental conditions.
When deployed, the camera’s internal processor or connected server performs the following analytical steps:
| Process Stage | Function | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Detection | Identifies whether an object within the frame is biological or environmental. | Binary classification: animal / no animal |
| Localization | Draws bounding boxes around detected animals. | Object coordinates within image |
| Classification | Determines species using pattern, color, and shape features. | Species label + confidence score |
| Counting | Identifies and counts multiple individuals within one frame. | Numeric output |
| Individual Recognition (advanced) | Compares unique identifiers such as coat patterns, scars, or stripe configurations. | Individual ID match |
| Behavioral Analysis (optional) | Evaluates movement and posture to infer feeding, resting, or alert states. | Behavior classification label |
This multi-stage process converts static imagery into structured ecological data that can support conservation, behavioral studies, and biodiversity management.
Species Recognition Accuracy
Species-level recognition is currently the most reliable function of AI-based wildlife cameras.
Studies using datasets from the Serengeti, Snapshot Wisconsin, and other camera-trap networks demonstrate species classification accuracy ranging from 85% to 97% under optimal conditions.
Accuracy depends on:
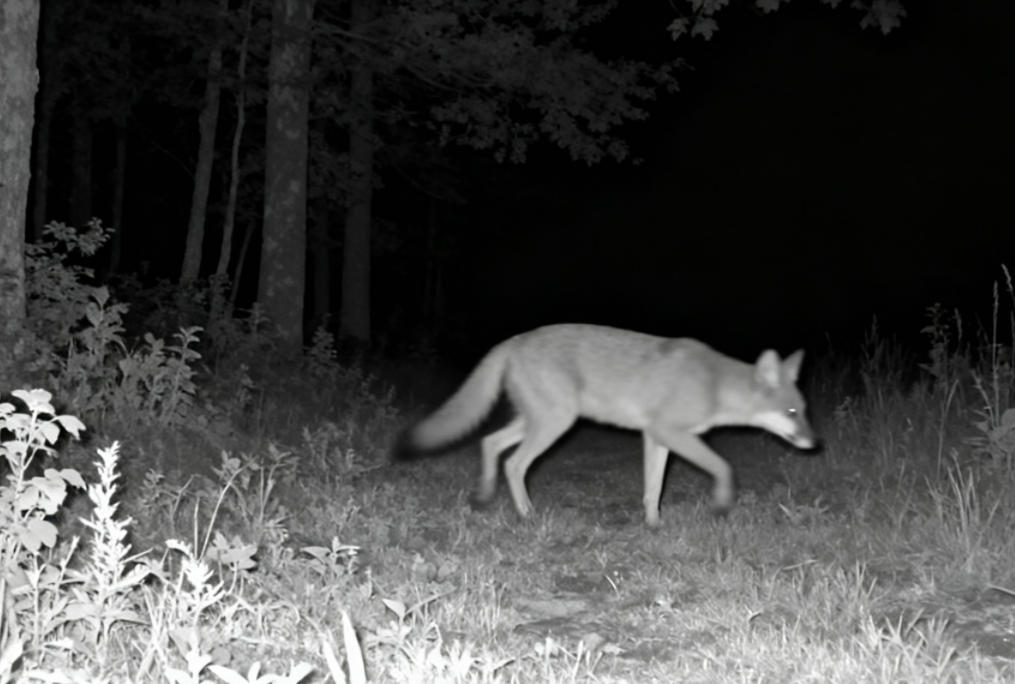

Image clarity and illumination (daylight vs. infrared).
Species distinctiveness (e.g., elephant vs. similar-looking antelope species).
Training data diversity — models perform better when exposed to multiple environments.
To enhance reliability, certain manufacturers incorporate edge AI chips, allowing real-time inference directly on the device without requiring cloud connectivity. This capability reduces power consumption and improves response time in remote areas.
Individual Animal Identification
Identifying specific individuals represents a more complex challenge.
Researchers use biometric pattern recognition, similar to human facial recognition, by analyzing features such as:
Stripe and spot patterns (tigers, leopards, zebras).
Ear shape, tusks, or horn curvature (elephants, deer).
Facial morphology (primates, bears).
AI models trained for these features can recognize individuals with 70–90% accuracy, depending on image consistency and dataset size.
This function is particularly valuable in population monitoring, migration tracking, and anti-poaching operations.
Application Scenarios
Ecological and Biodiversity Research
AI-assisted recognition allows large-scale data collection across time and geography, enabling researchers to map species distribution and analyze behavioral trends.
Conservation and Anti-Poaching
Real-time recognition systems can identify endangered species or detect unauthorized human presence. Alerts can be transmitted via 4G or satellite networks, improving response efficiency.
Agricultural and Livestock Monitoring
Outside conservation, similar technologies monitor livestock movement, identify intrusions by wild animals, and assess grazing behavior.
Industrial Implementation Example — Ringsee
Ringsee, a Chinese manufacturer specializing in security and wildlife monitoring equipment, integrates AI intelligent recognition in its solar-powered wildlife cameras.
These devices feature:
- Low-power operation with solar and battery supply.
- Edge computing capabilities for local AI inference.
- Adaptability to extreme outdoor environments.
Such designs are suitable for long-term field deployments without external power infrastructure.
Technical Challenges
Despite technological progress, several challenges persist:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Variability | Changes in lighting, weather, and vegetation affect model accuracy. |
| Data Labeling Limitations | Training datasets may be region-specific and lack rare species examples. |
| Computational Cost | High-performance AI models require substantial processing power and memory. |
| Ethical Considerations | Continuous surveillance may raise concerns about privacy when humans enter monitored areas. |
Future research focuses on improving transfer learning and cross-domain model adaptation to handle unseen species and diverse ecosystems.
Future Outlook
AI recognition in wildlife cameras is expected to evolve toward autonomous ecological monitoring networks.
Future systems may integrate:
- On-device learning, allowing models to improve automatically with new local data.
- Multi-sensor fusion, combining image, sound, and thermal data.
- Blockchain-based data verification, ensuring authenticity of wildlife records for research and conservation funding.
These innovations will transform camera traps from passive sensors into intelligent environmental observers.
Conclusion
Wildlife cameras equipped with AI recognition systems are capable of identifying animal species and, under certain conditions, recognizing individual animals.
This technology enhances efficiency, reduces manual image sorting, and supports conservation science with structured, high-quality data.
Manufacturers like Ringsee demonstrate how solar-powered, low-power AI cameras can extend these capabilities into remote habitats, merging advanced recognition with sustainable design.
As algorithmic accuracy and computing efficiency continue to improve, intelligent wildlife cameras will become indispensable tools for global ecological management and biodiversity preservation.
Prev:
Related News
Can Wildlife Cameras Recognize Specific Animals? The Rise of AI-Powered Detection in Conservation
Discover how AI-powered wildlife cameras are transforming animal recognition and species monitoring. Learn how intelligent camera systems—like those developed by Ringsee—can identify, classify, and even track individual animals to support global conservation efforts.
Oct 11,2025
How China’s Security Camera Market Is Evolving: Scale, Players, and Strategic Trends
In-depth analysis of China’s security camera market in 2025: market size, leading vendors, edge-AI and connectivity trends, OEM opportunities, and regulatory/export risks that shape global supply chains.
Oct 11,2025
How a 4G Solar Camera Protects Your Vacation Home Year-Round
Discover how 4G solar cameras keep your vacation home secure all year, even in remote areas without WiFi or power. Learn how Ringsee, a trusted Chinese manufacturer, offers reliable solar-powered security solutions for holiday homes.
Oct 10,2025
How Solar-Powered Wildlife Cameras Are Changing Conservation: What to Know & What to Buy
Explore how solar-powered wildlife cameras are transforming conservation and biodiversity research. Learn key buying tips, essential features, and discover trusted manufacturers like Ringsee—China’s expert in low-power solar wildlife monitoring systems.
Oct 10,2025
The Ultimate Guide to Solar Trail Cameras: Capturing Wildlife Without Hassle
In this guide, we cover everything you need to know: what features matter, how to choose the right model, practical tips for deployment, and real world examples of how solar wildlife cameras are already making a difference.
Oct 09,2025
Links:One Belt Power Technology
Add: 14th Floor, Baoshan Building, Longhua District, Shenzhen China.
Privacy Policy | SEO | CitySite | Support: 300.cn Dongguan
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.