Complete Guide to Security Camera Transmission Types: Wired, Wireless, and Beyond
Publish:
2025-05-30 10:11
Source:
https://www.ring-see.com
When building or upgrading a modern surveillance system, one of the most critical technical decisions you’ll make involves choosing the right transmission type. This refers to how a security camera sends its video (and sometimes audio) signals to a recording device, monitoring station, or cloud platform.
With the rapid advancement in surveillance technology, today’s security camera systems offer multiple transmission options, ranging from traditional analog to advanced fiber optic and 5G wireless. Understanding these transmission types will help you make an informed decision based on the unique needs of your installation environment—whether it’s for outdoor security, remote site surveillance, or smart home monitoring.
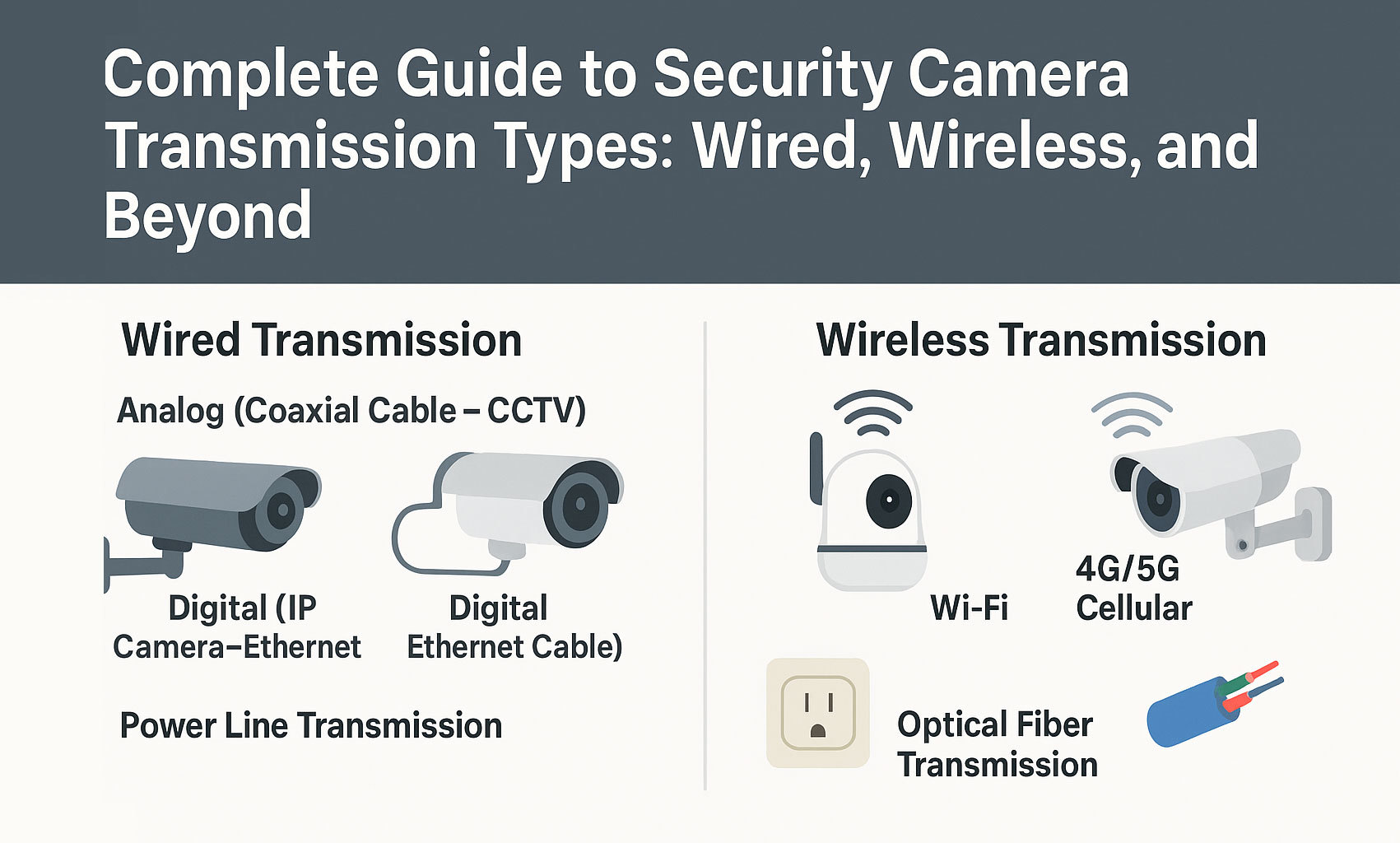
1. Wired Transmission Types for Security Cameras
Wired transmission remains the most stable and secure method for delivering video data. There are two main wired types: analog (coaxial) and digital (IP/Ethernet).
a. Analog Transmission (Coaxial Cable – Traditional CCTV)
Analog transmission is the foundation of conventional CCTV camera systems. It sends video signals through coaxial cables like RG59 or RG6.
Common Formats: CVBS (standard definition), HD-CVI, HD-TVI, and AHD (high definition)
Video Quality: Basic systems support 480p–720p, while HD analog standards can reach 1080p or even 4MP
Key Features:
Affordable hardware and installation costs
No IP configuration required
Typically used in legacy commercial surveillance systems
Limitations:
Lower image quality than modern IP systems
No intelligent analytics or remote access features
Separate cables needed for audio and control signals
b. Digital Transmission (IP Cameras over Ethernet)
IP (Internet Protocol) cameras are widely used in professional and home surveillance setups. They transmit digital data via Ethernet cables (Cat5e, Cat6), enabling high-definition video and intelligent functions.
Common Technologies: PoE (Power over Ethernet), NVR (Network Video Recorder) systems
Video Quality: 1080p, 4MP, 4K, and beyond
Key Features:
High-resolution, real-time video streaming
Easy integration with cloud storage and mobile apps
Supports AI video analytics, facial recognition, motion alerts, and more
Centralized or distributed system management
Limitations:
Requires network setup and security protocols
More bandwidth-intensive than analog systems
Dependent on switch/router capacity
2. Wireless Transmission Options
Wireless transmission offers flexibility in environments where cable installation is difficult or not possible. Two popular types are Wi-Fi and cellular (4G/5G) connections.
a. Wi-Fi Cameras (Wireless IP Security Cameras)
Wi-Fi transmission uses standard wireless networks to transmit video signals without physical cables.
Standards: IEEE 802.11 b/g/n/ac
Best for: Home security, retail stores, temporary setups
Advantages:
Quick and easy installation
Minimal cabling; only power is required (or can be battery-powered)
Integrates with smart home ecosystems
Drawbacks:
Signal interference from walls, other devices, or congestion
Limited to the range of the Wi-Fi network
Vulnerable to hacking without proper encryption
b. 4G/5G Cellular Security Cameras
4G security cameras and the newer 5G-enabled surveillance systems offer wireless transmission via mobile networks.
Best suited for: Remote locations, construction sites, farms, wildlife monitoring, off-grid properties
Benefits:
No dependency on local internet or Wi-Fi
Works wherever mobile signal is available
Often includes battery and solar-powered designs
Challenges:
Higher latency compared to Wi-Fi or Ethernet
Requires SIM card with data plan
Ongoing mobile data fees
Needs a strong and stable mobile signal
3. Power Line Communication (PLC) for Security Cameras
PLC (Power Line Communication) allows data to be transmitted over the existing electrical wiring in a building. It’s ideal when installing new Ethernet or coaxial cables is impractical.
Standards: HomePlug AV, G.hn
Typical Applications: Older buildings, apartments, offices with limited cable pathways
Advantages:
Leverages existing electrical outlets for network connectivity
Avoids major renovations or drilling
Disadvantages:
Performance varies depending on electrical wiring quality
Susceptible to signal noise from appliances and circuit interference
4. Fiber Optic Transmission (Enterprise-Level Surveillance)
Fiber optic is the gold standard for high-capacity, long-distance video transmission. It's used in critical infrastructure projects and expansive commercial or city-wide surveillance networks.
Best used for: Industrial security, airports, smart cities, multi-building campuses
Core Benefits:
Lightning-fast data rates with ultra-low latency
Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Supports extremely long transmission distances (up to several kilometers)
Drawbacks:
Higher installation cost
Requires specialized tools and expertise
Not necessary for most small to medium surveillance setups
Comparison Table of Transmission Types
| Transmission Type | Medium | Best Use Case | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog (Coaxial) | Coaxial cable | Legacy CCTV, budget installations | Low cost, easy to install | Limited resolution and features |
| Digital (IP) | Ethernet (Cat5e/Cat6) | Homes, businesses, smart security | High resolution, PoE, smart analytics | Needs network setup and bandwidth management |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless LAN | Home or office, DIY setups | Easy install, flexible placement | Signal interference, bandwidth limits |
| 4G/5G | Cellular network | Remote/off-grid locations | No internet needed, solar-compatible | Data fees, requires strong signal |
| Power Line (PLC) | Electrical wiring | Cable-limited indoor environments | Uses existing power lines | Electrical noise can affect signal |
| Fiber Optic | Fiber optic cable | Enterprise and long-distance surveillance | Highest quality and reliability | Expensive, complex to install |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Transmission Type for Your Security Camera System
Whether you're setting up a residential security camera, expanding a commercial surveillance network, or deploying a solar-powered 4G camera in a remote area, the right transmission type is key to system performance, reliability, and scalability.
Here’s a quick guide:
Choose Analog if you're upgrading legacy systems or working with a limited budget.
Go with Digital IP (PoE) for high-quality footage and smart features.
Opt for Wi-Fi when flexibility and convenience are priorities.
Use 4G/5G when local network infrastructure is unavailable.
Select PLC for indoor retrofits where running new cables isn't feasible.
Deploy Fiber Optic for enterprise-grade systems that demand long-range, high-capacity performance.
Each transmission type serves a specific purpose. By evaluating your project's size, location, and goals, you can implement a security solution that’s both effective and future-ready.
Related News
Why 4G Solar Security Cameras Are the Best Choice for Remote Surveillance in 2025
In many places, setting up security cameras is straightforward—connect to WiFi, plug into power, and you’re good to go. But what if you’re on a farm, at a construction site, or managing property far from reliable infrastructure?
Jun 05,2025
How Lens Quality, Focal Length, and Image Processing Impact Security Camera Image Clarity
Discover how lens quality, focal length, and image processing influence the performance of outdoor security cameras. Learn how to choose the best surveillance system for sharper, high-resolution footage.
Jun 03,2025
Complete Guide to Security Camera Transmission Types: Wired, Wireless, and Beyond
When building or upgrading a modern surveillance system, one of the most critical technical decisions you’ll make involves choosing the right transmission type. This refers to how a security camera sends its video (and sometimes audio) signals to a recording device, monitoring station, or cloud platform.
May 30,2025
Digital Zoom vs. Optical Zoom in Security Cameras – Which One Should You Choose?
Learn the difference between digital zoom and optical zoom in security cameras. Find out which zoom type suits your surveillance needs and get expert advice from Ringsee.
May 29,2025
Why Sensor Quality Matters More Than Megapixels in Security Cameras: What You Really Need to Know
When choosing a security camera, most customers look at resolution first — 2MP, 5MP, even 4K. But here’s the truth: megapixels alone don’t guarantee better video quality. What actually determines how clear, detailed, and reliable your footage is — especially at night — is the sensor inside the camera.
May 27,2025